
Transnational Organized Crime
Definition and Scope Transnational organized crime is a multifaceted phenomenon that encompasses various types of criminal activities. The United Nations Convention against Transnational Organized Crime (UNTOC) defines an organized criminal group as a "structured group of three or more persons, existing for a period of time and acting in concert with the aim of committing one or more serious crimes or offences." The scope of transnational organized crime is
read more →
International Fugitive
Definition and Classification International fugitives can be classified into different categories based on the nature of their crimes and the level of threat they pose. Some common categories include: - Terrorists: Individuals who have committed acts of terrorism and are fleeing to avoid prosecution. - Cybercriminals: Individuals who have committed cybercrimes such as hacking, identity theft, and online fraud. - Financial criminals: Individuals who have committed financial crimes such as money laundering,
read more →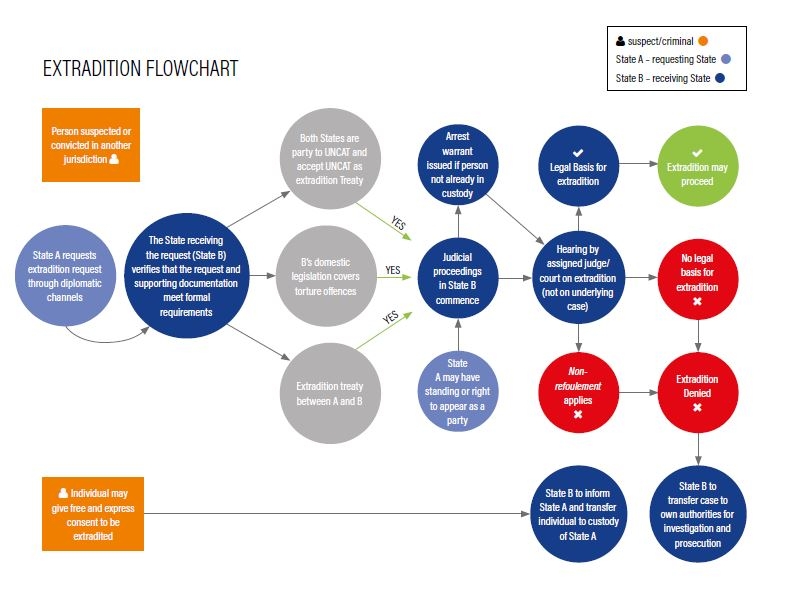
International Cooperation in Extradition
Background and History The concept of extradition has its roots in ancient times, with evidence of extradition agreements dating back to the Roman Empire and other ancient civilizations. However, modern extradition practices are based on a complex framework of international treaties and domestic laws that have evolved significantly over the centuries. The development of international law and the establishment of the United Nations have played pivotal roles in standardizing
read more →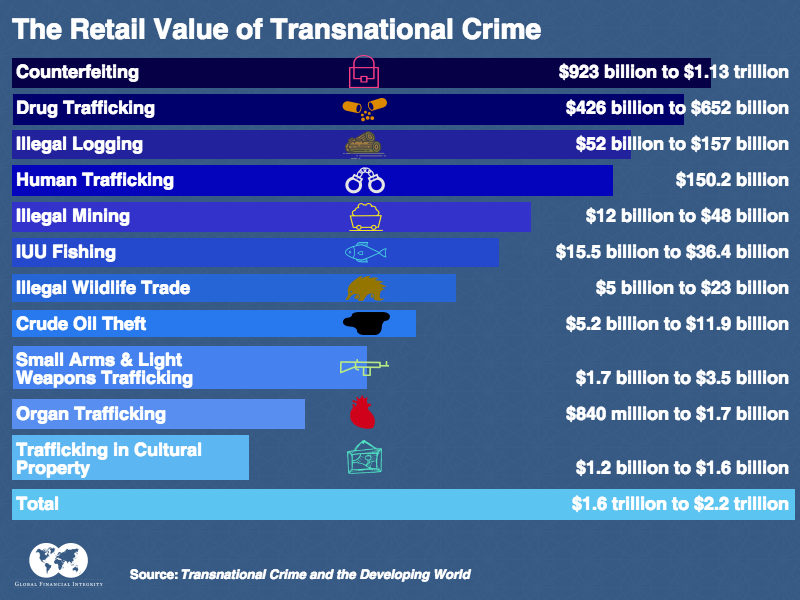
International Extradition and International Law
Definition and Principles of International Extradition International extradition is the formal process by which one country transfers an individual to another country to face trial or punishment for crimes committed. This process is based on the principle of mutual legal assistance, which requires countries to cooperate with each other in the pursuit of justice. The principles of international extradition are rooted in international law, including the United Nations Convention
read more →