International Cooperation in Extradition
by Admin
Posted on 12-05-2025 07:52 PM

Background and History
The concept of extradition has its roots in ancient times, with evidence of extradition agreements dating back to the Roman Empire and other ancient civilizations. However, modern extradition practices are based on a complex framework of international treaties and domestic laws that have evolved significantly over the centuries. The development of international law and the establishment of the United Nations have played pivotal roles in standardizing extradition procedures and promoting cooperation among nations.
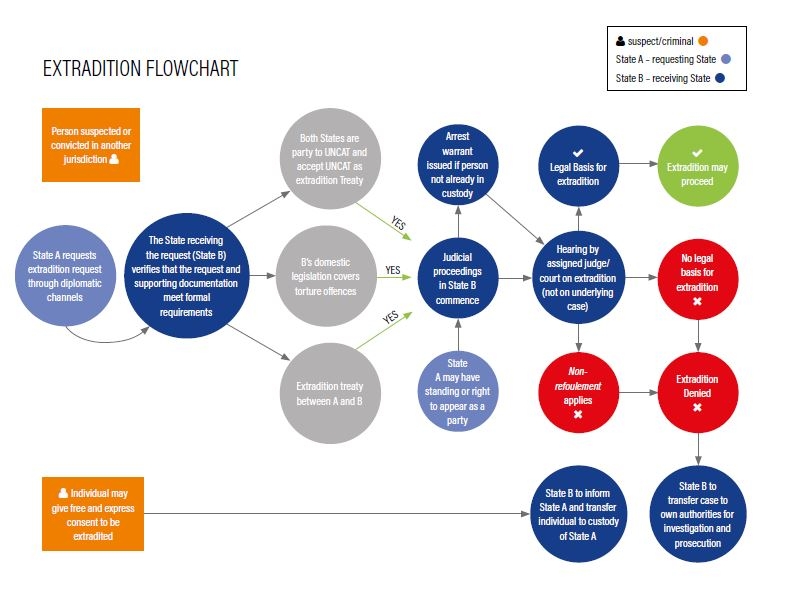
Legal Framework
The legal framework for extradition is primarily based on bilateral and multilateral treaties. These treaties specify the conditions under which one country can request the extradition of an individual from another country. The most common requirements include dual criminality (the act must be a crime in both countries), non-political offenses (extradition is not granted for political crimes), and humanitarian considerations (protection against torture or capital punishment). Domestic laws of each country also play a crucial role, as they outline the procedural aspects of extradition, including the rights of the individual and the judicial review process.
Bilateral Treaties
Bilateral extradition treaties are agreements between two countries that outline the terms and conditions for extradition. These treaties are tailored to the specific needs and legal systems of the participating countries, allowing for more detailed and customized arrangements. For instance, the treaty between the United States and the United Kingdom includes provisions for the extradition of fugitives, the transfer of sentenced persons, and cooperation in criminal matters.
Multilateral Treaties
Multilateral treaties, on the other hand, involve more than two countries and aim to establish common standards and procedures for extradition. Examples include the European Convention on Extradition and the United Nations Convention against Transnational Organized Crime. These treaties facilitate cooperation among a larger number of countries, simplifying the extradition process and enhancing the fight against international crime.
Challenges and Controversies
Despite the importance of international cooperation in extradition, several challenges and controversies arise. One of the significant issues is the differing legal standards and human rights protections across countries. This can lead to controversies when a country with strict human rights protections is asked to extradite an individual to a country with a questionable human rights record. Additionally, the political nature of some crimes and the potential for misuse of the extradition process for political purposes can complicate relations between nations.
Political and Human Rights Considerations
Political considerations and human rights concerns often intersect in extradition cases. For example, the request to extradite a person who might face the death penalty or torture in the requesting country can pose a dilemma for the country from which extradition is sought. International law and many national laws prohibit extradition in such circumstances, highlighting the need for careful consideration of human rights in the extradition process.
Mechanisms for Cooperation
Mechanisms for international cooperation in extradition include diplomatic channels, international organizations, and law enforcement agencies. The use of these mechanisms facilitates the exchange of information, coordination of efforts, and mutual legal assistance, which are essential for effective extradition.
Role of International Organizations
International organizations such as Interpol play a critical role in facilitating cooperation among law enforcement agencies worldwide. Interpol issues red notices, which are international wanted persons alerts, to help member countries identify and provisionally arrest individuals pending extradition. This and other initiatives by international organizations have significantly enhanced the efficiency of the extradition process.
Case Studies
Several high-profile cases illustrate the complexities and successes of international cooperation in extradition. For example, the extradition of fugitives from the United States to face trial in other countries, and vice versa, demonstrates the application of extradition treaties and the cooperation between law enforcement agencies across borders. These cases often involve intricate legal and diplomatic negotiations, underscoring the importance of robust international cooperation.
Future Directions
The future of International Cooperation in Extradition will likely be shaped by technological advancements, evolving international law, and the increasing recognition of the need for global cooperation in combating transnational crime. As criminals become more sophisticated in using technology and exploiting legal loopholes, the international community must adapt and strengthen its mechanisms for cooperation to ensure that the extradition process remains effective.
Conclusion
International cooperation in extradition is a vital component of global efforts to combat crime and ensure justice. Through treaties, agreements, and collaborative efforts, countries can work together to apprehend fugitives and bring them to justice, regardless of where they attempt to hide. As the world becomes increasingly interconnected, the importance of this cooperation will only continue to grow, necessitating ongoing efforts to improve and expand extradition mechanisms.
FAQs
What is the purpose of an extradition treaty?
Extradition treaties are designed to facilitate cooperation between countries in the transfer of individuals who have committed crimes in one country and are found in another, ensuring that criminals cannot escape justice by fleeing across borders.
How does the extradition process work?
The extradition process typically involves a request from one country to another for the transfer of a fugitive, followed by a legal review to ensure that the request meets the criteria outlined in the relevant extradition treaty and domestic laws.
What are some challenges in the extradition process?
Challenges include differing legal standards, political considerations, human rights concerns, and the potential for abuse of the extradition process for political purposes.
Can a country refuse an extradition request?
Yes, a country can refuse an extradition request if it does not meet the criteria outlined in the relevant treaty or domestic law, or if there are concerns about the potential treatment of the individual in the requesting country.
What role do international organizations play in extradition?
International organizations like Interpol facilitate cooperation among member countries by issuing international wanted persons alerts and providing a platform for the exchange of information and coordination of efforts in law enforcement.